The Heating, Ventilation, Air Conditioning, and Refrigeration (HVAC/R) industry is experiencing a profound transformation driven by artificial intelligence. Between 2022 and 2025, leading Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) have strategically integrated AI solutions across their product lines and operational workflows, resulting in measurable business impacts and competitive advantages.
As AI technologies mature, HVAC/R original equipment manufacturers are leveraging these tools to enhance system performance, optimize energy consumption, improve indoor air quality, and deliver unprecedented operational efficiencies. Moreover, advancements in AI are transforming the very way products are developed, streamlining HVAC equipment design and revolutionizing HVAC CAD drafting, which allows for faster, more precise prototyping and simulation of complex systems. This blog post delves into the specific applications, verified business outcomes, technical implementation strategies, and future trajectories of AI in the HVAC/R sector, providing valuable insights for industry professionals navigating this technological revolution.
The State of AI Adoption in HVAC/R Original Equipment Manufacturers
The integration of artificial intelligence within HVAC/R systems has accelerated dramatically since 2022. Industry leaders have moved beyond exploratory phases to full-scale implementation, with varying degrees of AI maturity across different geographic markets and company sizes.
AI Maturity Level and Market Geography
The AI adoption journey for HVAC/R original equipment manufacturers typically progresses through several phases:
- Data infrastructure development – Building sensor networks and setting up data collection systems
- Basic analytics implementation – Implementing simple data monitoring and pattern detection systems
- Advanced algorithm deployment – Using advanced algorithms for predicting maintenance needs and optimizing operations
- Autonomous control integration – Integrating systems that adjust themselves automatically
The table below summarizes the key players in the industry.
| Company | Region |
|---|---|
| Modine Manufacturing | US |
| Lennox International | US |
| Trane Technologies | US |
| Belimo | US/UK |
| BrainBox AI | US/Canada |
| Sensibo | Canada |
| Distro | Canada |
| Waabi | Canada |
| Carrier Global | US |
| Daikin | Canada |
| AAON | US |
| Honeywell | US |
| Mitsubishi Electric | UK |
| LG Electronics | UK |
| York International | US |
| Panasonic | UK |
| Rheem | US |
| Fujitsu | UK |
| Johnson Controls | US |
| Siemens Smart Infrastructure | UK |
| United Technologies | US |
| Viking Cold Solutions | US |
| Trane Canadian Operations | Canada |
Core AI Applications Transforming HVAC/R Original Equipment Manufacturers Operations
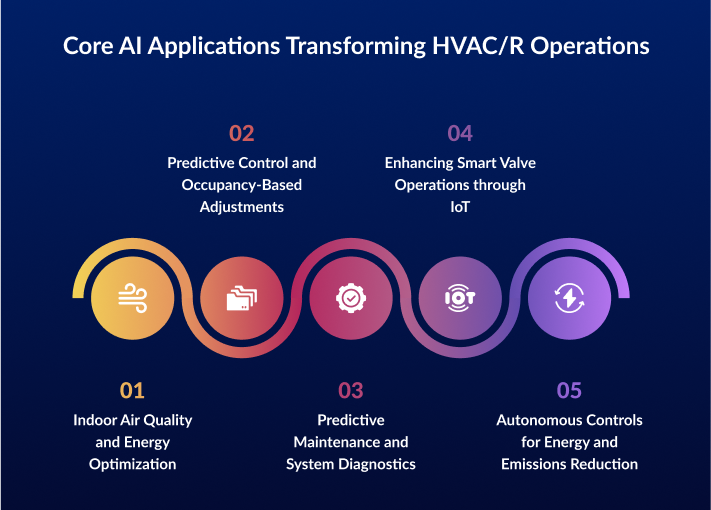
The documented implementations of AI across HVAC/R original equipment manufacturers focus on several key applications, each delivering specific operational benefits and efficiency improvements.
1.Indoor Air Quality and Energy Optimization
The modern HVAC/R original equipment manufacturers has focused its AI efforts on improving indoor air quality (IAQ) and energy efficiency. The integration of AI allows for adjustments in HVAC performance to maintain healthy indoor environments while consuming less energy. This aligns with wider trends where indoor environmental quality is critical, especially post COVID-19.
Modern AI-powered IAQ systems integrate multiple data streams:
- Particulate matter concentrations (PM2.5, PM10)
- Volatile organic compound (VOC) levels
- Carbon dioxide concentrations
- Humidity and temperature measurements
- Occupancy patterns and density
2.Predictive Control and Occupancy-Based Adjustments
Companies today have started implementing AI for occupancy prediction, a technique that adjusts HVAC operations based on real time occupancy data. This method increases efficiency by reducing wastage when spaces are unoccupied and ensures optimal comfort when occupied.
This predictive approach represents a significant advancement over traditional schedule-based controls, allowing systems to adapt to variable occupancy patterns and unexpected changes in building usage.
3.Predictive Maintenance and System Diagnostics
AI is deployed across multiple crucial areas, with predictive maintenance being one of the most impactful. The algorithms analyze sensor data and historical maintenance records to predict component failures before they even happen.
Predictive maintenance systems are used to detect the following:
- Vibration patterns in compressors and motors
- Temperature differentials across heat exchangers
- Pressure fluctuations in refrigerant lines
- Power consumption anomalies
- Acoustic signatures of operating equipment
By detecting subtle changes in these parameters, machine learning models identify patterns that precede equipment failure, allowing for intervention before costly breakdowns occur. This proactive strategy saves downtime and repair costs while prolonging equipment lifespan.
4.Enhancing Smart Valve Operations through IoT
Belimo has leveraged AI in collaboration with Facilio, focusing on smart valves that enhance building operational efficiency. The collaboration aims to integrate real-time operational data into a smart management platform, contributing to overall IoT-driven efficiency improvements in BMS.
These intelligent components communicate with central building management systems to coordinate operations across the entire HVAC network. Smart AI valves automatically adjust your HVAC flow based on real-time conditions, so you don’t have to spend time fiddling with settings that do the work for you!
5.Autonomous Controls for Energy and Emissions Reduction
BrainBox AI has been instrumental in demonstrating how autonomous, AI-driven HVAC systems can achieve significant energy cost savings and emissions reductions. Their technology is reported to reduce energy consumption by up to 25% and greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions by up to 40%, further underlining the potential of AI in enhancing sustainability.
Autonomous HVAC control systems operate on reinforcement learning principles (a type of machine learning where systems learn by trial and error from feedback), where the AI continuously optimizes its control strategies based on feedback from the environment.
This approach allows systems to continuously improve their performance over time, adapting to changing conditions and optimizing for multiple objectives simultaneously.
Technical Implementation Challenges – HVAC/R Original Equipment Manufacturers
Despite the compelling benefits, HVAC/R manufacturers face significant technical challenges when implementing AI solutions.
1.Data Quality and Integration
Effective AI performance depends on a foundation of consistent, accurate data. Many existing HVAC/R installations lack comprehensive sensor networks or use proprietary communication protocols that complicate data collection.
Manufacturers must address:
- Sensor calibration and drift compensation
- Data normalization across diverse equipment types
- Integration of legacy systems with modern data platforms
- Handling missing or corrupted data points
- Standardizing communication protocols
2.Algorithm Development and Validation – Original Equipment Manufacturers
Developing effective AI algorithms for HVAC/R applications requires domain-specific expertise and rigorous validation.
Key challenges include:
- Creating accurate thermal models for diverse building types
- Accounting for complex interactions between system components
- Validating algorithm performance across varied operating conditions
- Balancing competing objectives (energy efficiency, comfort, equipment longevity)
- Ensuring algorithm stability during edge cases and unusual conditions
3.Cybersecurity Considerations
As HVAC/R systems become more connected and intelligent, they also become potential targets for cyber attacks.
Manufacturers must implement:
- Secure communication protocols
- Regular security updates and patches
- Authentication and access control systems
- Data encryption for sensitive information
- Intrusion detection and prevention mechanisms
The cybersecurity challenge is especially important for critical infrastructure installations where HVAC/R systems may be connected to broader BMS networks.
Future Trajectories: The Next Evolution of AI in HVAC/R Original Equipment Manufacturers
As we look beyond 2025, these are the emerging trends that will likely shape the continued evolution of AI in the HVAC/R industry:
1. Edge Computing and Distributed Intelligence
The shift in AI processing from centralized cloud platforms to edge devices (small computing devices installed directly on HVAC/R equipment that process data locally instead of in the cloud) will increase.
This architectural shift offers several advantages:
- Reduced latency for real-time control decisions
- Continued operation during network outages
- Lower bandwidth requirements for data transmission
- Enhanced privacy through local data processing
- Reduced cloud computing costs
Leading manufacturers are already developing compact, energy efficient computing modules capable of running sophisticated AI algorithms directly on equipment controllers.
2.Digital Twin Integration
Digital twin technology (virtual models of real systems), used to test and optimize performance, is converging with AI to enable advanced simulation and optimization. These virtual models are inherently parametric in nature, allowing engineers to observe and analyze real-time changes in critical system variables including temperature, pressure, speed, flow rates, and power consumption. This capability enables precise monitoring and dynamic adjustment of system performance across all operational conditions.
These virtual replicas can:
- Simulate real time system performance under varied conditions, showing exactly how changing parameters like supply air temperature, refrigerant pressure, or fan speeds affects overall system efficiency and comfort delivery
- Test control strategies before deployment by manipulating virtual parameters to predict actual system responses without risking physical equipment or disrupting building operations
- Identify optimization opportunities through parametric analysis that reveals ideal operating ranges for temperature setpoints, pressure levels, and component speeds to maximize efficiency and minimize energy consumption
For example, it can diagnose complex system interactions by tracing how parameter changes in one subsystem (like a chiller) cascade through the entire system, affecting connected components (like air handlers or terminal units)
By leveraging these parametric capabilities, digital twins provide HVAC/R engineers with powerful tools for understanding system dynamics, optimizing performance, and developing more intelligent control strategies that respond effectively to changing conditions.
3.Cross-System Integration and Optimization
In the future, AI will coordinate and optimize multiple building systems that traditionally operated independently of each other.
Its capabilities include:
- Coordinating HVAC operation with lighting systems based on occupancy
- Integrating renewable energy generation with thermal storage
- Optimizing building envelope components alongside mechanical systems
- Participating in grid demand response programs
- Coordinating multiple buildings within campus or district systems
This holistic approach will unlock efficiency opportunities beyond what can be achieved by optimizing HVAC/R systems in isolation.
Strategic Recommendations for HVAC/R Original Equipment Manufacturers Technical Leaders
Design engineers, CTOs, and technical teams working in HVAC/R manufacturing are driven to implement AI adoption to gain competitive advantages through improved product performance, reduced warranty claims, and enhanced energy efficiency, while simultaneously creating new revenue streams through predictive maintenance services and meeting growing demands for sustainable building solutions that deliver superior indoor environmental quality.
To achieve this, several strategic priorities emerge:
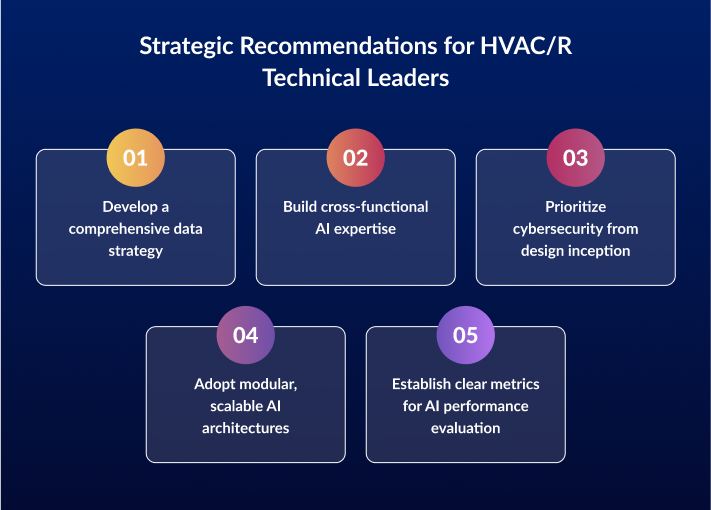
- Develop a comprehensive data strategy
- Audit existing data collection capabilities
- Standardize data formats and communication protocols
- Implement robust data validation and cleaning processes
- Establish clear rules for managing and protecting data that balance utility with privacy
- Leverage AI-driven tools for HVAC equipment design and HVAC CAD drafting to accelerate prototyping and enhance design precision
- Build cross-functional AI expertise
- Cultivate internal talent through training and recruitment
- Establish partnerships with AI technology providers
- Create collaborative teams combining domain experts with data scientists
- Develop processes for algorithm validation and performance monitoring
- Prioritize cybersecurity from design inception
- Implement security-by-design principles in product development
- Conduct regular vulnerability assessments
- Develop secure update mechanisms for deployed systems
- Create incident response protocols for potential breaches
- Adopt modular, scalable AI architectures
- Design systems that can evolve with advancing AI capabilities
- Implement standardized APIs for component integration
- Create frameworks that support both cloud and edge processing
- Develop testing environments that simulate diverse operating conditions
- Establish clear metrics for AI performance evaluation
- Define key performance indicators aligned with business objectives
- Implement continuous monitoring of AI system effectiveness
- Create feedback mechanisms for algorithm improvement
- Develop transparent reporting on AI contribution to business outcomes
Conclusion
From Competitive Advantage to Industry Necessity
The integration of AI into HVAC/R manufacturing has shifted from being a competitive advantage to an industry necessity. Leading OEMs are already using AI to optimize air quality, energy efficiency, and system performance, achieving measurable improvements in operations, customer satisfaction, and market differentiation. Verified results ranging from significant revenue contributions and higher adoption rates to sustainability gains like energy reduction and emission cuts make it clear that AI delivers both financial and environmental value.
Looking ahead, the question is no longer whether to adopt AI, but how to execute it effectively. Manufacturers that focus on strong data strategies, advanced algorithms, cybersecurity, and workforce readiness will be best positioned to lead this transformation. With rising capital investments and growing industry collaboration, AI is setting the foundation for a more efficient, resilient, and sustainable HVAC/R future.